WSO2 API Manager recently added a feature to control the visibility and the management of the API publisher interface which allows multiple teams within a same organization to independently develop their APIs without allowing others to edit or modify APIs. Even though separate teams can achieve the same (or higher) level of isolation through multi tenancy, it is not a viable option for most user scenarios where they need to expose APIs through the same tenant without dealing with the tenant level complexities.
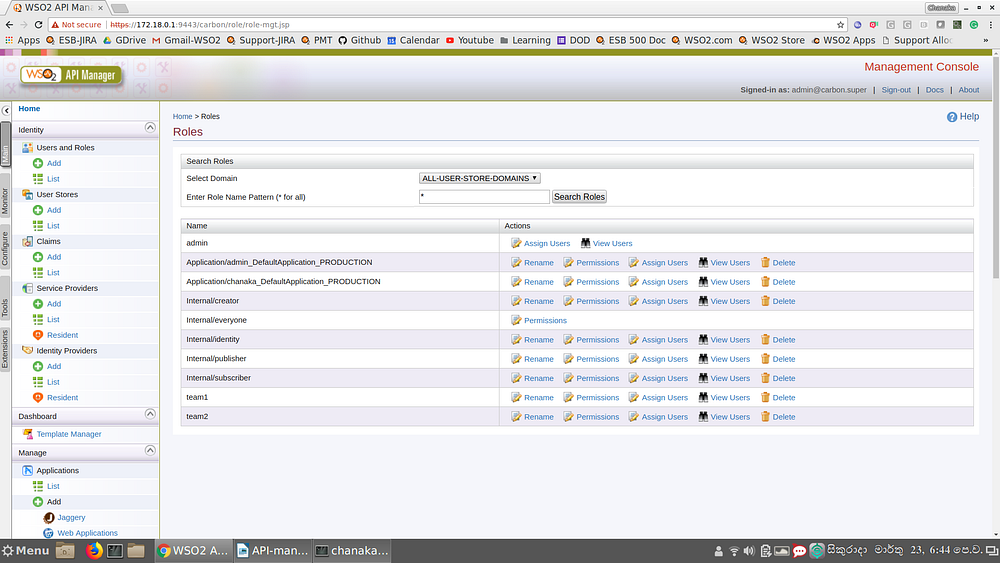
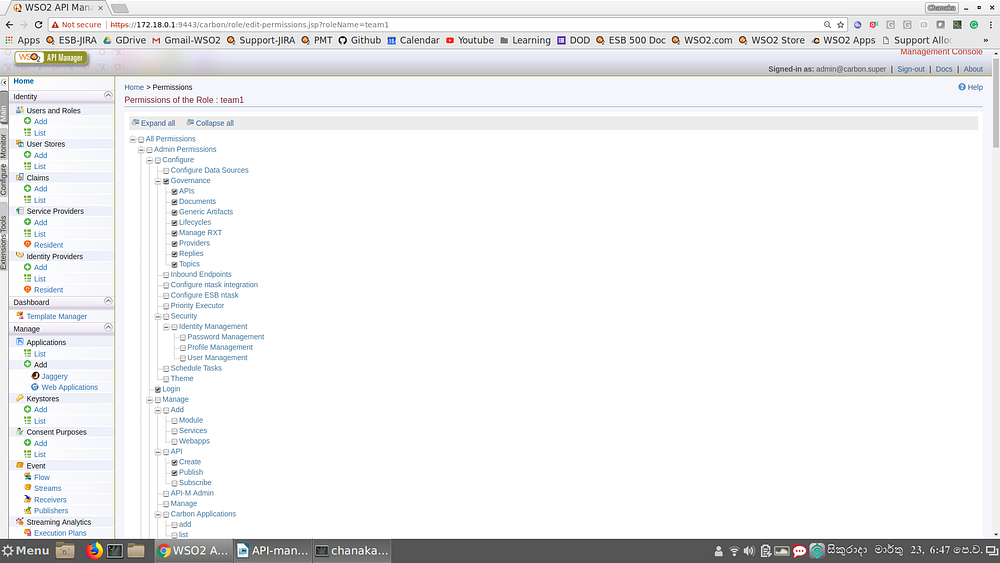
The basic requirement to achieve team level isolation is to create a role per team with necessary permissions to create and publish APIs. You can do this by log in to the WSO2 API manager carbon console (https://localhost:9443/carbon) and then creating a role for team1 and then assigning API creation and publishing permissions.
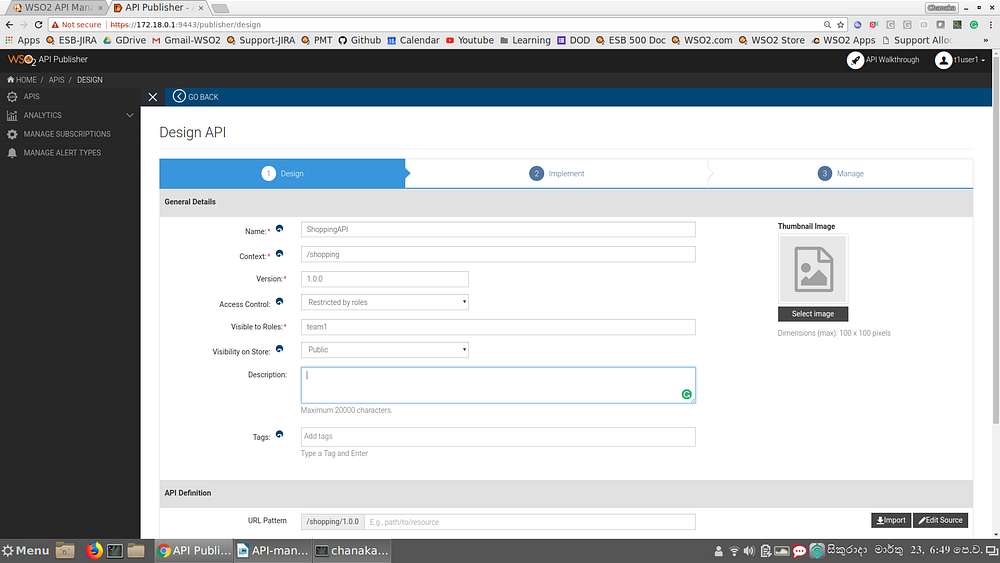
Once this role is created, the team members related to team1 can be assigned to this role. Once we do that, APIs created by any of the team member of team1 can select the team1 role as the Access control→Restricted by roles option of publisher when creating the APIs so that the API can only be visible in the publisher portal to any other team members in the same team only (+admin).
If the team members in another team (group) creates an API, those APIs will not be visible to the members of the team1 within the publisher portal (if they follow the same steps mentioned above). This will make the team level isolation during the API development time.
Even though these APIs are not visible within the publisher portal, the visibility on the Store portal can be different. When the API is created, user can select the visibility level at the store. That can be done at
- Role based
- Tenant domain based
- Public
Depending on the selected visibility level of the Store side, other team members might also be able to view the API within the store. But they cannot modify the API since it is not visible at the publisher side.
Using this method, an organization can easily manage their multiple API development teams without interfering with each other. This feature is available with API Manager 2.1.0 latest updates.
Nice and good article. It is very useful for me to learn and understand easily. Thanks for sharing your valuable information and time. Please keep updating mulesoft Online Training
ReplyDeleteI really enjoy the blog.Much thanks again. Really Great salesforce online course
ReplyDeleteAPI Development Company UK,
ReplyDeleteCustom API Development Company Lucknow India,
Top Web Services and API Development Company Lucknow,
Real Estate Web Development Lucknow India,
API Development Company in UK,